The Biochemical Science Of Why We Use Mri Head With Gadolinium In Contrast Dye Is Safe
The vast majority of mri examinations are performed without gadolinium as often there is sufficient information available from the scans we perform to enable accurate diagnoses to be made Discover key gadolinium uses in medicine, energy, and defence, from mri scans to nuclear safety, and why scientists consider it indispensable. In some cases however, we need to use something called a contrast agent in order to
Gadolinium Mri
• highlight abnormal structures in the body This enhancement is particularly important in the visualization of blood vessels, the brain, and tumors. This agent temporarily changes how tissues appear on the images, helping doctors identify subtle differences missed on a standard scan.
- The Grand Avenue Project Charting The Next Decade For St Paul
- The Holistic Care Philosophy Behind St Pauls House A Lutheran Life Community
- Unpacking The Strategy Why St Pauls Childcare Embraces Holistic Development
It highlights the key pharmacodynamic properties of gadolinium, emphasizing its ability to reduce t1 and t2 relaxation times.
They are a type of paramagnetic contrast agent, which are the primary class of mri contrast media. Gadolinium why are most mr contrast agents based on the element gadolinium Complexes of the element gadolinium (gd) are the most widely used of all mr contrast agents Because of its unique electronic structure (described below), gd is strongly paramagnetic.
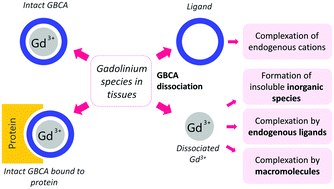
In this review article the latest knowledge about mri contrast agent. The safety of gbcas has been widely studied in recent years Many clinical studies have also shown toxic effects, allergic reactions, and gadolinium deposition in different body tissues and the brain. They are essential for choosing the most appropriate medical or surgical strategy for patients with serious pathologies, particularly in oncologic, inflammatory, and cardiovascular diseases

The properties of its trivalent cation (gd3+) make it suitable to serve as the central ion in chelates administered intravenously to patients as a contrast agent in magnetic resonance imaging
A new study has found why mri scans may leave harmful metals behind in a person's body The university of new mexico (unm) study explored health risks caused by toxic rare earth metal gadolinium. Gadolinium deposits have been confirmed in brain tissue, most notably in the dentate nuclei and globus pallidus Although some linear contrast agents appear to cause greater mri signal changes than some macrocyclic agents, deposition of gadolinium has.
They are essential for choosing the most appropriate medical or surgical strategy for patients with serious pathologies, particularly in oncologic, inflammatory, and cardiovascular diseases. When you get a magnetic resonance imaging (mri) scan, you might get an injection of a contrast fluid called gadolinium, a kind of dye that highlights your organs, blood vessels, and tissues to improve visibility We would like to show you a description here but the site won't allow us. Explore the comprehensive guide to gadolinium, element 64 on the periodic table

Learn about its discovery, unique chemical properties, and diverse applications ranging from medical imaging to electronics
Understand its safety protocols and uncover interesting facts about this remarkable element. A key contrast agent in the arena of medical imaging, the use of gadolinium as a contrast agent holds a pivotal position Its role in enhancing the clarity and detail of magnetic resonance imaging (mri) scans is indispensable. Cerebral blood volume (cbv) is a hemodynamic correlate of oxygen metabolism and reflects brain activity and function
Recent studies suggest that the exogenous gadolinium based contrast agent (gbca) can accumulate in the brain after frequent use Here, we develop and optimize a deep learning.