The Surprising Discrepancies In Gcs Neuro Scoring Between Modern Clinicians Glasgow Coma Scale Made Nursemathmedblog 45% Off
In this narrative review, we have analyzed seven studies published between 2009 and 2024 in hopes of highlighting some of the limitations, such as potential subjectivity in scoring, inability to assess certain brainstem reflexes, and the need for supplementary assessments for specific neurological conditions. In fact, no individual clinical or patient feature has the granularity to capture the full spectrum of tbi severity [4]. The glasgow coma scale (gcs) was introduced in 1974 at the university of glasgow by neurosurgery professors dr
Comparison of current research focuses between clinicians and basic
Bryan jennett to assess the extent of neurological dysfunction in acute medical and trauma patients. Although the gcs sum score has been shown to correlate with patient outcome, any individual sum score can be derived from different combinations of the three components of the gcs, each with varying prognostic value [3] First described in 1974 by graham teasdale and bryan jennet, 1 the glasgow coma scale (gcs)—and the subsequently derived glasgow coma score—ended up becoming one of the most commonly used clinical tools in medicine
- The Great Debate Parents React To Saint Paul Schools 2026 Homework Policy Shift
- Viral Tiktok Clips From Hershey Coed Soccer Championship Final Games
- Sustainable Cities And Green Tech Building A Resilient Future Society
Since its initial publication, the gcs has been incorporated into numerous clinical guidelines and scoring systems for the evaluation of impairment of consciousness in acute.
The glasgow coma scale (gcs) is the most widely recognized clinical tool used to evaluate consciousness after a brain injury In emergency medicine and neurology, it serves as a universal language that allows doctors, nurses, and first responders to describe a patient's level of responsiveness quickly and consistently. Background statement accurate completion of a neurological assessment including the glasgow coma scale (gcs) is of the upmost importance in identifying and escalating neurological deterioration. Abstract background the glasgow coma score (gcs) is a clinical tool used to measure level of consciousness in traumatic brain injury and other settings
Despite its widespread use, there are many inaccuracies in its reporting Introduction the glasgow coma scale (gcs) is widely applied in the emergency setting It is used to guide trauma triage and for the application of essential interventions such as endotracheal intubation Concerns regarding the accuracy and validity of gcs.

Conclusions this study demonstrated that fluctuations in gcs scores are inversely associated with fluctuations in cox
As cox increases (impaired autoregulation), more severe neurological impairment is observed However, the difference in cox between high and low gcs is small and warrants further studies investigating this association. However, the gcs scale does not have brainstem assessment, which is required in the assessment of neurological deterioration in patients with. Furthermore, these discrepancies highlight the need for enhancing the training of both prehospital and emergency department clinicians in gcs assessment practices
Educational initiatives focused on standardizing evaluation criteria and techniques could help mitigate the variability observed in gcs scoring. The gcs was designed for the objective measurement of level of consciousness, assessment of trend, and to facilitate accurate and valid communication between clinicians Concerns have been raised about the potential for misleading levels of precision engendered by the use of the gcs, and the use of simpler scales suggested This review discusses the gcs and conditions affecting calculation of.

After 40 years, the glasgow coma scale (gcs) is the resource of choice for assessing the level of consciousness in patients with neurological conditions
Clinicians' ability to monitor patients' conditions, identify deterioration and make clinical decisions depends on their ability to carry out gcs assessments, so it is vital that they. With the objective of using the gcs in the emergency setting to accomplish optimal triage of tbi patients, the present study analyzed individual gcs component scores and categorized misjudged factors of gcs scores by means of a video examination in which the most common gcs scores of emergency trauma patients were simulated. We would like to show you a description here but the site won't allow us. The glasgow coma scale (gcs) characterizes patients with diminished consciousness
In a recent systematic review, we found overall adequate reliability across different clinical settings, but reliability estimates varied considerably between studies, and methodological quality of studies was overall poor. To investigate whether the glasgow coma scale (gcs) can be used reliably and accurately by inexperienced observers, ratings made by observers grouped … The glasgow coma scale[1] (gcs) is a clinical diagnostic tool widely used since the 1970s to roughly assess an injured person's level of brain damage The gcs diagnosis is based on a patient's ability to respond and interact with three kinds of behaviour

Eye movements, speech, and other body motions.
Objective to evaluate interobserver reliability of intensive care unit patients' glasgow coma scale scores Methods this prospective observational study evaluated glasgow coma scale scoring agreement among 21 intensive care unit nurses and 2 independent researchers who assessed 202 patients with neurosurgical or neurological diseases. Abstract and figures after 40 years, the glasgow coma scale (gcs) is the resource of choice for assessing the level of consciousness in patients with neurological conditions. The glasgow coma scale (gcs) provides a structured method for assessment of the level of consciousness
Its derived sum score is applied in research and adopted in intensive care unit scoring systems. Purpose examining the impact of scoring aids on the accuracy of assessing the glasgow coma score (gcs) in a standardized trauma scenario (primary outcome) Evaluating physicians' understanding of the gcs assessment and clinical application (secondary outcome) Materials and methods this randomized trial was performed at the simulator center of a swiss tertiary academic medical hospital.
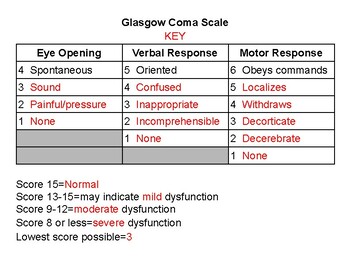
What is the glasgow coma scale
The glasgow coma scale (gcs) is a system to score or measure how conscious you are It does that by giving numbered scores for how awake you are, your level of awareness and how you respond to basic instructions.






