Radiomics: The 2026 Oncology Breakthrough Using Predictive Data Models Board Members
This study aimed to improve response prediction in hgsoc patients undergoing nact by integration different feature selection methods. Its objective is to discern nuanced radiomic attributes that are challenging to detect by mere observation [13, 14]. This review aims to describe the applications of radiomics in rt, including its methodology and the potential predictive and prognostic value (figure 1)
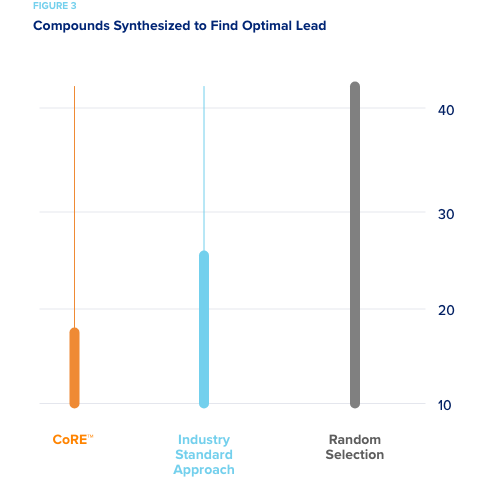
CORE case studies - Predictive Oncology
Radiomics is especially beneficial for treatment response assessment, prognosis of disease progression, and monitoring minimal residual disease Radiomics employs sophisticated data modeling algorithms to extract meaningful features from extensive imaging datasets, facilitating a profound quantitative assessment of lesion heterogeneity The session also discusses the combination of machine learning and artificial intelligence, which further improves feature extraction, predictive modeling, and pattern recognition.
- New Data Reveals Saint Pauls School Alumni Dominate 2026 Tech Unicorn Leadership
- Aa County Youth Basketball New Aacrp Initiatives Reshape 2026 Player Development
- The Shocking Truth Behind St Pauls Admissions 2026 Sees Record International Surge
Background radiomics investigation strategies can be applied to head and neck tumours, including lesion segmentation, tumour grading and staging prediction
Texture features from pet/ct radiomics, particularly those reflecting metabolic heterogeneity within the primary tumour, have shown substantial predictive value for lymph node metastasis in oral cancer Hait sees the use of artificial intelligence (ai) in radiomics—using data science to extract quantitative features from clinical images like scans or slides—as a practical way to discriminate which of these pulmonary nodules in a scan could be problematic, thereby reducing false positives and unnecessary procedures. Radiomics has the potential to transform cancer management, whereby radiomics data can be used to aid early tumor characterization, prognosis, risk stratification, treatment planning, treatment response assessment, and surveillance Both preclinical models and patient data are useful sources for the discovery of predictive biomarkers, and several publicly available collections exist that can also support biomarker investigations.
Radiomics models exhibit moderate diagnostic performance in predicting kras mutations in lung cancer Future efforts should strictly adhere to relevant guidelines, strengthen model validation, and standardize workflows to enhance the practical value of radiomics in precision oncology. A predictive biomarker enables clinicians to make an informed management choice by identifying patients who would benefit from a particular therapeutic agent Radiomics and deep learning models were examined to predict the os time by analyzing the gtv, clinical ctv, and ctvmodel

The study involves 126 subjects for model development and 62 independent subjects for testing.
This review highlights the transformative impact of ai in lung cancer management, discusses crucial barriers such as model bias and fairness, and outlines future directions for clinical application. This is a new approach to discovery in 2023 25 published a radiomics and deep learning fusion model for lung cancer subtype prediction. Additionally, a total of 3375 radiomics features were extracted, and 7 key features were selected for model construction
Compared with the image group model and clinical model, the nomogram model based on imaging group had the best predictive performance (training group auc 0.894, sensitivity 83.72%, speci city 84.00%, fi Explore the asco meeting program guide for comprehensive information on sessions, speakers, and topics at asco's upcoming meetings. Moreover, building predictive models based on the lack of standardized radiomics features adds to this complexity and challenges the employed ml algorithms

In order to address these issues and obtain optimal reproducibility gains, careful methodological and statistical consideration of the potential pitfalls is necessary.
With the continuous upgrading of computer technology, deep learning, as a breakthrough technology in artificial intelligence, has shown good performance and great potential in the application of nsclc prognostic models. The standard workflow of radiomics consists of (1) study design, (2) collection and curation of images and associated contextual data, (3) identification and delineation of objects of interest (eg, organs, tumors), (4) extraction of features (intensity, shape, textural, deep) and (5) modeling (ie, train and validate multiparametric models. This review aims to explore the synergy between three key omics domains



![[PDF] Optimized Predictive Models in Health Care Using Machine Learning](https://img.perlego.com/book-covers/4335822/9781394175352_300_450.webp)



